Rene Descartes Biography and Quotes: Life with Documentary

- Publisher: ZiHow Workshop
- Genre: Reference
- Released: 20 Jul, 2016
- Size: 78.2 MB
- Price: $2.99
 Click here to request a review of this app
Click here to request a review of this app
- App Store Info
Description
Want to learn All about Rene Descartes biography and quotes, and to watch his documentary all in one App? This is for you.Features:
- Visualized history and biography, for easy learning and reference
- Famous Quotes to get inspiration
- Documentary or speeches to bring you virtually back to the history
- Having everything about Rene Descartes in one App.
Brief Introduction of Rene Descartes:
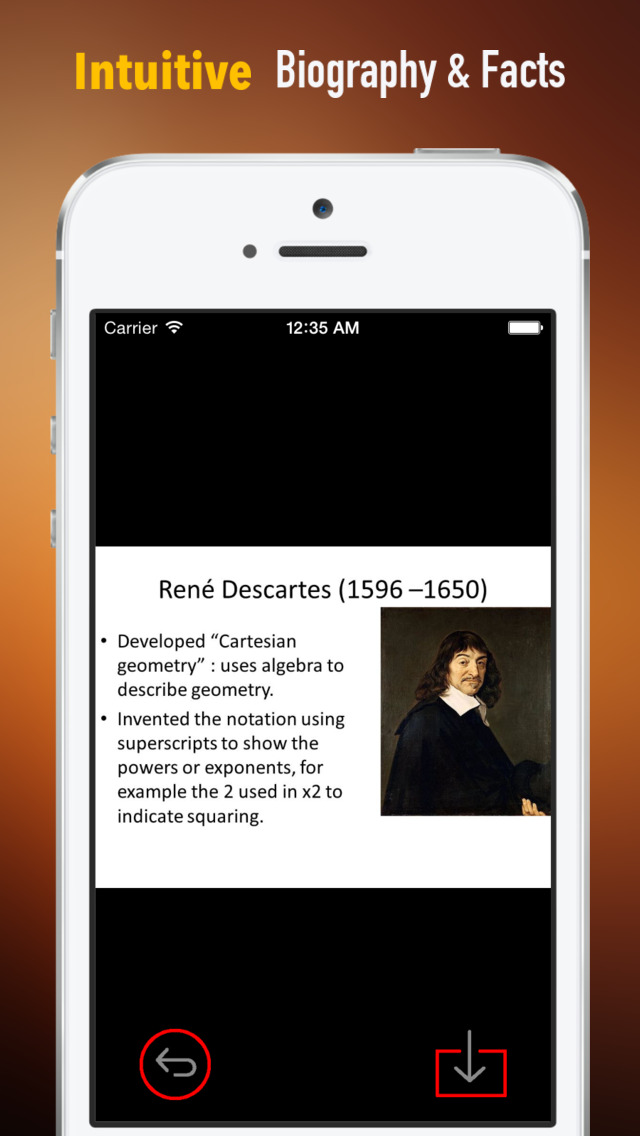
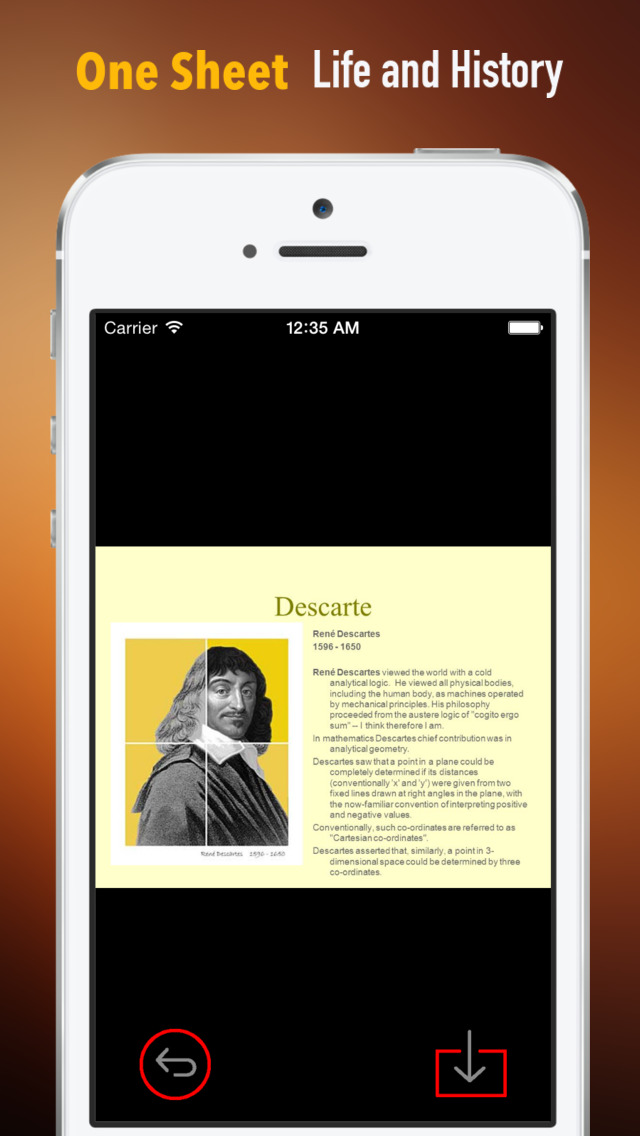
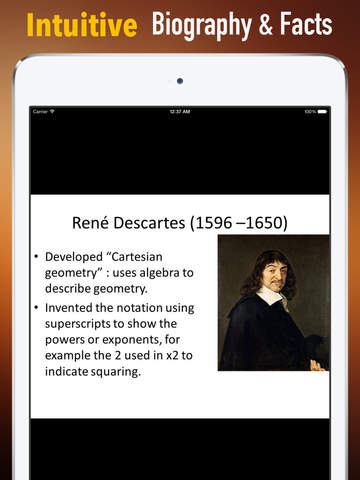
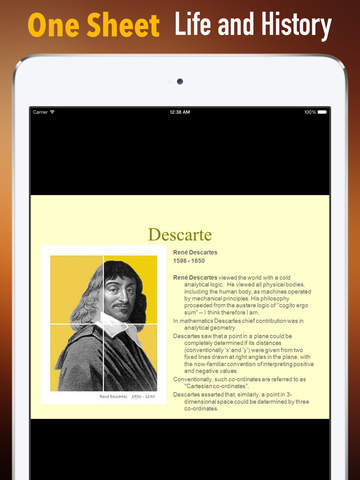
Rene Descartes was a French philosopher, mathematician, and scientist. Dubbed the father of modern western philosophy, much of subsequent Western philosophy is a response to his writings, which are studied closely to this day. He spent about 20 years of his life in the Dutch Republic.
Descartes's Meditations on First Philosophy continues to be a standard text at most university philosophy departments. Descartes's influence in mathematics is equally apparent; the Cartesian coordinate system—allowing reference to a point in space as a set of numbers, and allowing algebraic equations to be expressed as geometric shapes in a two- or three-dimensional coordinate system (and conversely, shapes to be described as equations)—was named after him. He is credited as the father of analytical geometry, the bridge between algebra and geometry, used in the discovery of infinitesimal calculus and analysis. Descartes was also one of the key figures in the scientific revolution.
Descartes refused to accept the authority of previous philosophers, and refused to trust his own senses. He frequently set his views apart from those of his predecessors. In the opening section of the Passions of the Soul, a treatise on the early modern version of what are now commonly called emotions, Descartes goes so far as to assert that he will write on this topic "as if no one had written on these matters before". Many elements of his philosophy have precedents in late Aristotelianism, the revived Stoicism of the 16th century, or in earlier philosophers like Augustine. In his natural philosophy, he differs from the schools on two major points: First, he rejects the splitting of corporeal substance into matter and form; second, he rejects any appeal to final ends—divine or natural—in explaining natural phenomena. In his theology, he insists on the absolute freedom of God's act of creation.
Descartes laid the foundation for 17th-century continental rationalism, later advocated by Baruch Spinoza and Gottfried Leibniz, and opposed by the empiricist school of thought consisting of Hobbes, Locke, Berkeley, and Hume. Leibniz, Spinoza and Descartes were all well-versed in mathematics as well as philosophy, and Descartes and Leibniz contributed greatly to science as well.
We look forward your feedback and comment to improve your experience with this application.